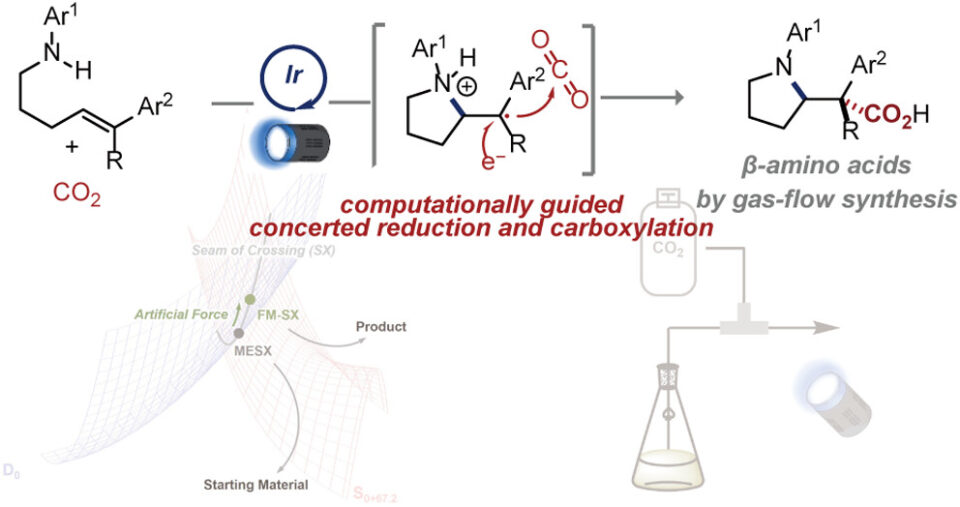
β-Amino acids are important building blocks in organic chemistry and particularly valuable in pharmaceutical and artificial peptide research. Nonetheless, their current production methods have strict limitations. CO2 as a feedstock for the installation of carboxyl units is highly desired for its abundance, low cost, and low toxicity. This has been successfully integrated in both α- and γ-amino acid synthesis, however, β-amino acid synthesis relies on substrate structures to provide the carboxyl unit.
To this end, a research group led by Professor Mita and Professor Maeda at WPI-ICReDD, Hokkaido University, has developed a new synthetic method for β-amino acid synthesis using CO2 through quantum chemical calculations and experimentally demonstrated its efficacy. Furthermore, in collaboration with Professor Mase’s group at the Research Institute of Green Science and Technology at Shizuoka University, they developed a gas-liquid flow synthesis with this reaction, enabling continuous and efficient production of β-amino acids.
Guided by their quantum chemical calculations, their strategy produces β-amino acid derivatives from aminoalkenes and CO₂ under mild conditions, using blue LED irradiation in the presence of a photo-activated catalyst. Their flow system demonstrated high yields after merely 3 minutes. This article is open access and available to everyone!