A new method streamlines the design and effectiveness of ligands used in chemical reactions in catalysis and drug delivery.
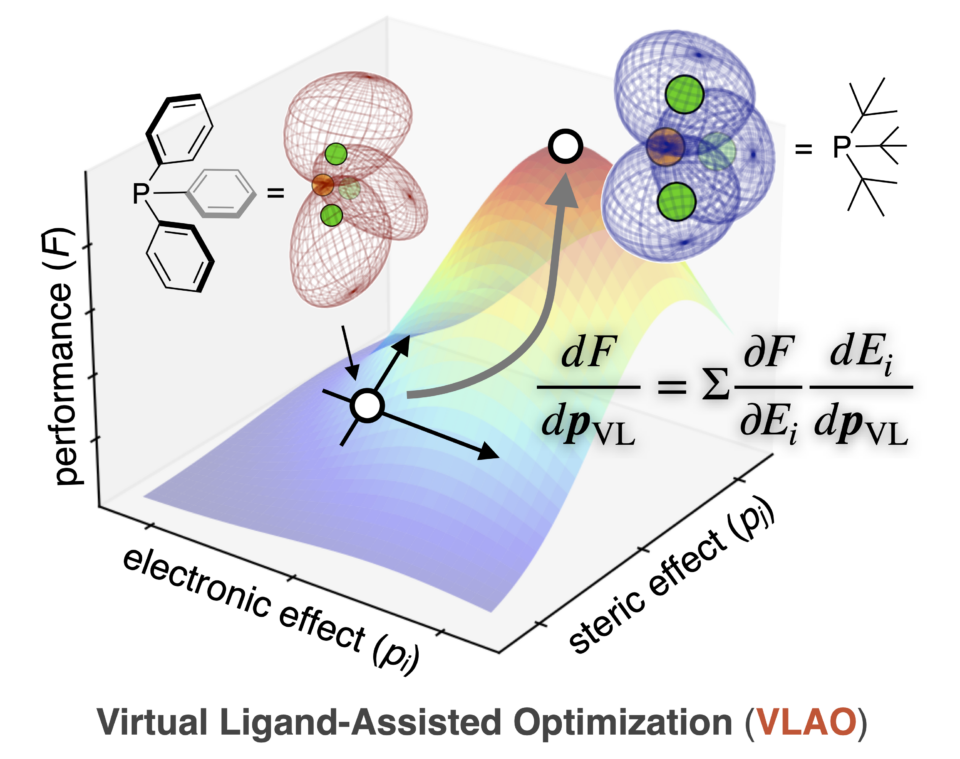
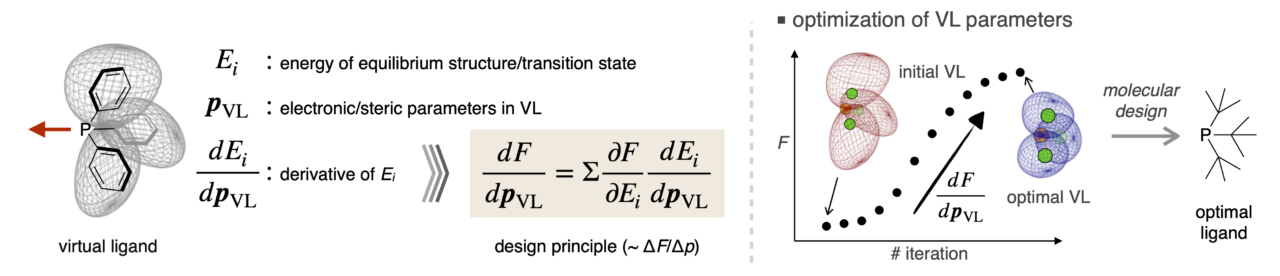
Researchers at Hokkaido University in Japan have developed a technique called Virtual Ligand-Assisted Optimization, or VLAO, to enhance the design and effectiveness of ligands, which are important molecules used in chemical reactions, especially in catalysis. The study, published in the journal ACS Catalysis, details the new approach that streamlines the complex and time-consuming process of ligand engineering.
Ligands bind to central metal atoms during chemical reactions, influencing how these metals interact with other substances. Properties such as their size, shape, and charge can greatly affect the speed of reactions and the types of products produced. Ligands are used in a wide range of domains, from industrial manufacturing to targeted medical therapies.
Optimizing ligands for a reaction has traditionally been a labor-intensive process. Scientists design ligands based on established measurements, such as the arrangement of electrons and the physical shape of the ligand. However, this approach needs extensive experimentation and often fails to capture complex correlations between ligand’s property and its performance in a target reaction, making it slow and challenging.
Read more >> (Hokkaido University’s Press Release)